The xBar System
Actionable insights based on post-operative tissue healing data

Sensors

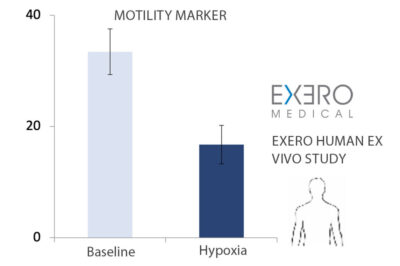
Tissue Healing Data
Clinician App
Clinical Evidence
A pivotal study of the xBar technology is underway.
Pilot Study
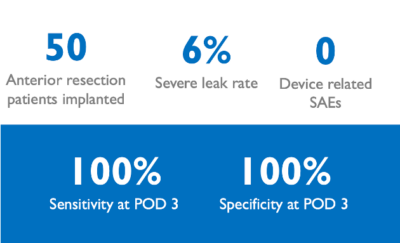
100% sensitivity and 100% specificity in detecting severe leaks at post-operative day 3
A multi-center pilot study of 50 anterior resection patients monitored with the xBar system post-operatively demonstrated leak detection with 100% sensitivity and 91.5% specificity at POD 2, and 100% sensitivity and 100% specificity at POD 3. In all instances, severe leaks were detected at least 2 days earlier by xBar compared to the clinical team.
This study demonstrates clinical feasibility of the xBar system. Read more about the study here.
A pivotal study to validate the safety and accuracy of the xBar system for early detection of major complications such as severe leaks is ongoing at eleven sites across the United States and Israel.
Scientific Publications

Post-operative monitoring of intestinal motility, ischemia, and inflammation for early detection of anastomotic leaks
The objective of this multi-center pilot study was to evaluate if this device can reliably detect anastomotic leaks earlier than the current standard of care.

Implantation of an Impedance Sensor for Early Detection of Gastrointestinal Anastomotic Leaks
Accurate early diagnosis of a gastrointestinal anastomotic leak remains a challenge. When an anastomotic leak develops, the electrical properties of the tissue undergoing inflammatory processes change, resulting from the extravasation of inflammatory fluid and cellular infiltration.

DEGRADABLE BIOSENSOR FOR THE EARLY DETECTION OF ABDOMINAL SEPSIS
Introduction: Postoperative abdominal sepsis is often a catastrophic event with huge clinical, organizational and economic impact.

Colonic Tissue Perfusion Assessment Using Local Electrophysiological Sensing
Verification of adequate perfusion is essential to ensure anastomosis integrity following colonic resections. Perfusion monitoring intra and postoperatively is challenging, and existing methods are unable to provide reliable perfusion metrics over time.